The cosmos is a vast and mysterious expanse, filled with wonders that ignite our curiosity and inspire our imaginations.
Among its most captivating phenomena are nebulae—vast clouds of gas and dust that serve as the birthplaces of stars and the remnants of stellar explosions. From the vibrant hues of emission nebulae to the delicate structures of planetary nebulae, each type tells a unique story about the life cycle of stars and the dynamic processes that shape our universe. In this blog post, we will embark on a journey through the cosmos, unveiling the different types of nebulae and exploring their significance in the grand tapestry of space. whether you’re a seasoned astronomer or a casual stargazer, join us as we delve into the stunning beauty and intricate details of these celestial wonders, illuminating the secrets they hold and the role they play in the ongoing saga of the universe.
1. Introduction to Nebulae: What Are They?
Nebulae are among the most captivating and enigmatic objects in the universe, serving as the celestial nurseries where stars are born and the remnants of stellar death. Derived from the Latin word for “cloud,” nebulae are vast clouds of gas and dust that float in the vast expanse of space. These cosmic formations can be found throughout the Milky Way and beyond, each with its unique characteristics and significance in the life cycle of stars.
At their core, nebulae consist primarily of hydrogen, helium, and other trace elements, forming intricate structures that can stretch for light-years. Some nebulae are illuminated by the light of nearby stars, creating breathtaking displays of color and luminosity, while others remain dark and invisible to the naked eye, only revealing their secrets through the instruments of modern astronomy.
Nebulae play a crucial role in the cosmic ecosystem. They are the sites where gas and dust coalesce to form new stars, a process that can take millions of years. Conversely, when massive stars exhaust their nuclear fuel, they explode in spectacular supernovae, dispersing their material across the cosmos, enriching the interstellar medium and allowing new nebulae to form.
In this blog post, we will embark on a journey through the cosmos, exploring the different types of nebulae—emission, reflection, planetary, and dark nebulae—each contributing to our understanding of the universe’s evolution and the life cycles of stars. As we delve into the fascinating world of these celestial clouds, we’ll uncover not only their beauty but also the vital roles they play in the grand tapestry of the cosmos.
2. The Importance of Nebulae in the Universe
Nebulae are not just beautiful cosmic clouds; they play a crucial role in the grand tapestry of the universe. These celestial formations serve as both nurseries and graveyards for stars, marking the cycles of stellar life and death that govern the cosmos. The importance of nebulae can be understood through several key functions they perform.
Firstly, nebulae are the birthplaces of stars. Comprised of gas and dust, these vast regions of space are where gravity begins to pull materials together, leading to the formation of new stars. The dense areas within a nebula, known as stellar nurseries, ignite the process of nuclear fusion, giving rise to brilliant new stars that will illuminate the universe for millions, if not billions, of years. The famous Orion Nebula is a prime example, showcasing vibrant colors and intricate structures as new stars emerge from its depths.
Conversely, nebulae also represent the remnants of stellar death. When massive stars exhaust their nuclear fuel, they undergo spectacular supernova explosions, ejecting their outer layers into space. This material becomes a new nebula, enriching the interstellar medium with heavy elements forged in the heart of the star. These elements are essential for the formation of planets, moons, and even life itself, illustrating how nebulae facilitate the recycling of cosmic material.
Furthermore, nebulae are vital for astronomical research. They provide insights into the physical processes that govern star formation and evolution. By studying the light emitted from nebulae, astronomers can glean information about the composition, temperature, density, and motion of these clouds, enhancing our understanding of the universe’s structure and dynamics.
In essence, nebulae are a fundamental part of the cosmic ecosystem—bridging the gap between stellar birth and death, offering a glimpse into the life cycles of the universe, and serving as a canvas for scientific discovery. As we continue to explore these magnificent structures, we uncover not only the secrets of star formation but also the very origins of the elements that make up our world.
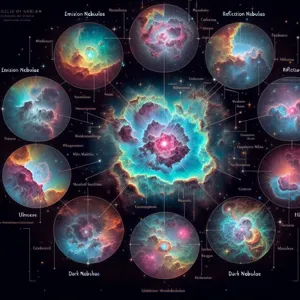
3. Types of Nebulae: An Overview
Nebulae, the stunning clouds of gas and dust scattered throughout our galaxy, come in a variety of forms, each playing a unique role in the cosmic tapestry. Understanding the different types of nebulae not only enriches our appreciation of their beauty but also sheds light on the processes of star formation and the lifecycle of celestial bodies.
### 1. Emission Nebulae
Emission nebulae are vibrant, glowing clouds that radiate their own light, primarily due to the ionization of gas within them. Often found in regions of active star formation, these nebulae are typically composed of hydrogen and helium, illuminated by the intense radiation from nearby young, hot stars. The Orion Nebula, one of the most studied emission nebulae, showcases a breathtaking array of colors, revealing the intricate structures formed by gas and dust.
### 2. Reflection Nebulae
In contrast to emission nebulae, reflection nebulae do not emit their own light but instead shine by reflecting the light of nearby stars. These nebulae often appear blue due to the scattering of light, similar to how the Earth’s atmosphere gives the sky its color. The Pleiades star cluster, with its delicate blue haze, is a perfect example of a reflection nebula, highlighting the interplay between starlight and cosmic dust.
### 3. Dark Nebulae
Dark nebulae are the elusive shadows of the cosmos, dense clouds of dust and gas that block the light from stars and other celestial objects behind them. These nebulae create striking silhouettes against the backdrop of brighter stars, giving them a mysterious appearance. The Horsehead Nebula, located in the constellation Orion, is one of the most iconic dark nebulae, captivating astronomers and stargazers alike with its unique shape and the secrets it holds within.
### 4. Planetary Nebulae
Despite their name, planetary nebulae have nothing to do with planets. Instead, they represent a late stage in the life of a star similar to our sun. As these stars exhaust their nuclear fuel, they expel their outer layers, creating a shell of glowing gas around a hot core. This process results in the formation of intricate and colorful structures, such as the Helix Nebula, often referred to as the “Eye of God.”
### 5. Supernova Remnants
Supernova remnants are the spectacular aftermath of a massive star’s explosion. When a star reaches the end of its life cycle, it can explode in a cataclysmic event, dispersing its outer layers into space. The Crab Nebula is one of the most studied supernova remnants, providing invaluable insights into the dynamics of stellar explosions and the recycling of materials in the universe.
Each type of nebula offers a glimpse into the complex processes that shape our universe, from the birth of stars to their explosive deaths. As we continue to explore and understand these celestial wonders, we not only expand our knowledge of the cosmos but also deepen our connection to the vast and intricate universe we inhabit.
4. Emission Nebulae: The Birthplaces of Stars
Emission nebulae are truly the celestial nurseries of the universe, vibrant and dynamic regions where stars are born. These stunning formations shine with a spectrum of colors, primarily reds and pinks, created by the ionization of gas—predominantly hydrogen—when it is energized by the intense radiation emitted from nearby young, hot stars. The process is a mesmerizing dance of light, where the ultraviolet rays from these nascent stars excite the surrounding gas, causing it to glow with an ethereal luminescence.
One of the most famous examples of emission nebulae is the Orion Nebula, located just 1,344 light-years away in the Orion constellation. This magnificent cloud of gas and dust is not only a visual delight but also a hotspot for stellar formation, harboring countless stars in various stages of their life cycles. As you gaze upon images of the Orion Nebula, the striking pink and red hues serve as a reminder of the cosmic forces at play, creating new stars that will one day illuminate the cosmos.
Emission nebulae are often found in regions where the interstellar medium—the matter that exists in the space between stars—is dense enough to facilitate the gravitational collapse needed for star formation. As these clouds of gas and dust condense, they gather into clumps, eventually forming protostars. Over millions of years, these protostars will continue to evolve, igniting nuclear fusion at their cores and ultimately becoming the stars that light up our night sky.
Beyond their role as stellar nurseries, emission nebulae also contribute to the richness of the universe’s chemical diversity. When massive stars reach the end of their life cycles and explode as supernovae, they disperse heavy elements back into the surrounding nebulae, enriching the interstellar medium with the building blocks for future generations of stars and planets. This cyclical nature of stellar birth and death underscores the interconnectedness of cosmic phenomena, revealing the intricate tapestry woven throughout the universe.
As we continue to explore these vibrant regions, astronomers are gaining new insights into the processes that govern star formation and the evolution of galaxies. Emission nebulae serve as a reminder of the beauty and complexity of the cosmos, inviting us to ponder our place within it and the myriad stars that illuminate the night sky.
5. Reflection Nebulae: Light from Nearby Stars
Reflection nebulae are one of the most captivating celestial phenomena in our universe, showcasing a beautiful interplay of light and dust. Unlike emission nebulae, which glow with their own light due to ionized gases, reflection nebulae do not produce light; instead, they reflect the light of nearby stars, creating a stunning canvas of colors and textures across the cosmos.
These ethereal clouds of gas and dust are often found surrounding young, hot stars, which emit a brilliant glow that illuminates the surrounding material. The light from these stars is scattered by the dust particles within the nebula, resulting in a soft, diffused glow that can range from pale blue to deep violet. The bluish hue often observed in reflection nebulae arises from Rayleigh scattering, the same phenomenon that makes our sky appear blue.
One of the most famous examples of a reflection nebula is the Witch Head Nebula, located in the constellation Eridanus. This striking formation is bathed in the light of the nearby star Rigel, showcasing a breathtaking display of shimmering dust and intricate structures. Another well-known example is the reflection nebula found within the Orion Nebula, where the interplay of light from the region’s young stars creates a mesmerizing and dynamic environment.
Exploring reflection nebulae not only reveals the beauty of the universe but also provides valuable insights into the processes of star formation. As dust and gas coalesce under gravity, they often give birth to new stars, making these nebulae a crucial part of the cosmic lifecycle. By studying these phenomena, astronomers can better understand the conditions that lead to star formation and the intricate relationships between stars and their surrounding environments.
In essence, reflection nebulae serve as both a visual feast for stargazers and a window into the dynamic processes that shape our universe. Their delicate beauty is a reminder of the complexity and wonder that exists beyond our planet, inviting us to ponder the mysteries of the cosmos and our place within it.
6. Dark Nebulae: The Cosmic Clouds of Dust
Dark nebulae, often described as the cosmos’ shadowy veils, are fascinating celestial structures composed primarily of dense clouds of gas and dust. These enigmatic formations are called “dark” because they absorb and block the light from stars and other luminous objects that lie behind them, creating striking contrasts against the backdrop of the universe.
Imagine gazing into the night sky and spotting a patch of darkness amidst the twinkling stars; that patch could very well be a dark nebula. These nebulae can be colossal, spanning many light-years, and their intricate shapes are often sculpted by the gravitational forces of nearby stars or the dynamic behavior of the interstellar medium.
One of the most famous examples is the Horsehead Nebula, a dark silhouette against the bright backdrop of the Orion constellation. Its distinct shape resembles a horse’s head, captivating astronomers and stargazers alike. Dark nebulae are not just beautiful to behold; they also play a crucial role in the formation of new stars. Within their dense cores, regions of gas and dust can collapse under their own gravity, eventually leading to the birth of new stars, planets, and even entire solar systems.
Studying dark nebulae allows astronomers to gain insights into the processes of stellar formation and the chemical evolution of the cosmos. These cosmic clouds serve as a reminder of the universe’s complexity, showcasing the delicate balance between light and darkness and the intricate dance of creation that continues to unfold in the depths of space. As we explore the cosmos, dark nebulae invite us to ponder the mysteries of the universe, challenging us to look beyond the visible and uncover the hidden wonders that lie in the shadows.
7. Planetary Nebulae: The Final Stage of Stellar Evolution

Planetary nebulae are one of the most enchanting phenomena in the cosmos, embodying the final act of a star’s life cycle. Contrary to what their name might suggest, these celestial wonders have nothing to do with planets; instead, they are the remnants of medium-sized stars like our Sun, which have reached the end of their nuclear burning phase. As these stars exhaust their nuclear fuel, they shed their outer layers into space, creating a stunning shell of gas and dust that glows with vibrant colors, often showcasing intricate structures and patterns.
The formation of a planetary nebula begins when a star like our Sun expands into a red giant, a stage characterized by its dramatic increase in size and brightness. During this phase, the star’s core contracts and heats up, eventually causing the outer layers to be expelled into the surrounding interstellar medium. This ejection of material can happen in pulses, resulting in a symmetrical structure or, in some cases, a more chaotic shape, depending on various factors such as magnetic fields and stellar winds.
What makes planetary nebulae particularly captivating is the interplay of light and color. The gas expelled from the star is ionized by the intense ultraviolet radiation emitted from the hot core that remains—known as the white dwarf. This ionization causes the gas to emit light across a spectrum of colors, creating breathtaking displays that can range from delicate blues and greens to fiery reds and oranges. Some of the most famous examples, like the Ring Nebula (M57) in the constellation Lyra or the Helix Nebula (NGC 7293) in Aquarius, showcase these vibrant hues, making them favorite targets for both amateur and professional astronomers.
As these nebulae evolve, they gradually disperse into the surrounding space, enriching it with the elements forged in the star’s core. This process plays a crucial role in the cosmic cycle of matter, contributing essential materials to the formation of new stars and planets. Thus, planetary nebulae are not just the end of one star’s life; they are a vital part of the ongoing story of the universe, illustrating the beauty and complexity of stellar evolution. Observing these intricate structures offers a glimpse into the past and a hint of the future, reminding us of the interconnectedness of all celestial bodies in the vast expanse of space.
8. Supernova Remnants: The Aftermath of Stellar Explosions
Supernova remnants are one of the most breathtaking phenomena in the cosmos, showcasing the dramatic aftermath of a star’s explosive death. When a massive star reaches the end of its life cycle, it detonates in a spectacular supernova event, ejecting its outer layers into space. This cataclysmic explosion not only marks the star’s demise but also gives rise to a vibrant and complex nebula—a cosmic tapestry woven with the remnants of stellar material.
These remnants are composed of a wide variety of elements, including carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and even heavier elements like iron and gold, which were forged in the star’s core during its lifetime. As the stellar material expands and cools, it interacts with the surrounding interstellar medium, creating intricate structures of gas and dust. The colors we see in images of supernova remnants—bright reds, blues, and greens—are the result of different elements emitting light at specific wavelengths, painting a vivid picture of the star’s explosive legacy.
One of the most famous examples of a supernova remnant is the Crab Nebula, the result of a supernova observed in 1054 AD. The Crab Nebula is a stunning showcase of swirling gas and filaments, with pulsar activity at its center, a rapidly rotating neutron star that emits beams of radiation. This remnant continues to be a focal point for astronomers, offering insights into the life cycles of stars and the dynamics of cosmic explosions.
Supernova remnants play a crucial role in the universe’s ecosystem, enriching the interstellar medium with heavy elements that will eventually contribute to the formation of new stars and planets. They serve as cosmic recycling centers, reminding us that in the vastness of space, destruction and creation are inextricably linked. As we explore these remnants, we not only witness the beauty of the universe but also gain a deeper understanding of the processes that govern stellar evolution and the life cycles of galaxies.
9. The Role of Nebulae in Galaxy Formation
Nebulae play a crucial role in the grand tapestry of galaxy formation, acting as both the nursery and the structured framework for stars and planetary systems. These vast clouds of gas and dust, often referred to as the building blocks of the universe, are where the magic of stellar birth takes place. Within the dense regions of a nebula, gravitational forces begin to dominate, causing particles to clump together and form protostars. This process is not instantaneous; it can take millions of years, highlighting the patience and elegance inherent in cosmic evolution.
As new stars ignite in a nebula, they emit intense radiation and stellar winds, which can impact the surrounding material in profound ways. The energy released by these young stars can trigger further star formation in adjacent areas of the nebula, creating a chain reaction that contributes to the dynamic architecture of galaxies. Moreover, the remnants of stars that have reached the end of their life cycles—through supernova explosions, for instance—inject heavy elements back into the nebula, enriching the interstellar medium. This process not only replenishes the nebula but also sets the stage for the formation of future generations of stars and planets, contributing to the ongoing cycle of cosmic creation.
The intricate interplay between nebulae and galaxy formation also reveals the diverse structures that galaxies can take. Spiral galaxies, for example, are often rich in nebulae, with their arms serving as regions of active star formation. In contrast, elliptical galaxies tend to have fewer nebulae and, as a result, fewer new stars, illustrating how different environments can shape the evolutionary paths of galaxies over billions of years. In essence, nebulae are not just beautiful cosmic phenomena; they are vital components of the universe’s architecture, influencing the birth, life, and death of stars, and ultimately, the evolution of galaxies themselves.
As we continue to explore the cosmos, understanding the role of nebulae will deepen our appreciation for the complexity and interconnectivity of the universe, reminding us that within these celestial clouds lies a story of creation, destruction, and rebirth that has unfolded over eons.
10. Famous Nebulae: A Tour of Notable Examples
When it comes to celestial wonders, nebulae stand out as some of the most intriguing and visually stunning formations in the cosmos. These clouds of gas and dust are not only beautiful but also serve as the birthplaces of stars and planets, playing a crucial role in the lifecycle of the universe. Join us as we embark on a tour of some of the most famous nebulae, each with its unique characteristics and captivating stories.
**1. The Orion Nebula (M42)**
Located in the Orion constellation, the Orion Nebula is one of the brightest nebulae visible to the naked eye and is a favorite among amateur astronomers. It lies about 1,344 light-years away from Earth and is a stellar nursery, where new stars are born from the dense clouds of gas and dust. With its vibrant hues of pink and blue, the Orion Nebula is a magnificent sight captured in countless photographs, showcasing the intricate details of its gaseous filaments and young stars.
**2. The Crab Nebula (M1)**
A remnant of a supernova explosion that was observed by Chinese astronomers in 1054 AD, the Crab Nebula is a fascinating example of a supernova remnant. Situated in the constellation Taurus, this nebula is notable for its complex structure and the pulsar at its center, which emits beams of radiation as it rotates. The Crab Nebula is a rich source of information for astronomers studying the life cycles of stars and the mechanics of supernova explosions, making it an essential object of research in astrophysics.
**3. The Ring Nebula (M57)**
Found in the constellation Lyra, the Ring Nebula is a stunning example of a planetary nebula. Its characteristic doughnut shape and striking colors are the result of a dying star shedding its outer layers, while its core collapses into a white dwarf. Situated about 2,000 light-years from Earth, the Ring Nebula offers a glimpse into the final stages of stellar evolution, making it a crucial piece of the cosmic puzzle.
**4. The Lagoon Nebula (M8)**
The Lagoon Nebula is a vast and vibrant region of star formation located in the constellation Sagittarius. Spanning about 110 by 50 light-years, this emission nebula is home to a stellar nursery where new stars are forming, surrounded by glowing gas and dark dust lanes. The Lagoon Nebula is particularly striking in astronomical images, showcasing a variety of colors that highlight the different elements present within the gas.
**5. The Horsehead Nebula (B33)**
Perhaps one of the most iconic nebulae, the Horsehead Nebula is renowned for its distinctive silhouette resembling a horse’s head. Nestled in the Orion constellation, this dark nebula is a region of dense dust and gas, obscuring the stars behind it. It captures the imagination of stargazers and photographers alike, serving as a reminder of the beauty and mystery that the universe holds.
These famous nebulae not only serve as breathtaking sights in the night sky but also provide valuable insights into the processes of star formation and the evolution of the universe. Each nebula tells a story—of creation and destruction, of birth and death—reminding us of the dynamic and ever-changing nature of the cosmos. As we continue to explore these celestial wonders, we deepen our understanding of our place in the universe and the remarkable phenomena that surround us.
11. Observing Nebulae: Tips for Amateur Astronomers
Observing nebulae can be an awe-inspiring experience, offering a glimpse into the vast and mysterious universe that surrounds us. For amateur astronomers eager to explore these celestial wonders, a few tips can significantly enhance your observations and deepen your understanding of these cosmic formations.
First and foremost, choose the right equipment. While some nebulae can be admired with the naked eye on particularly clear nights, a good pair of binoculars or a telescope will provide a much more detailed view. Telescopes with at least an aperture of 4 inches (100 mm) are ideal for capturing the intricate details and colors of brighter nebulae. Consider using a filter, like a UHC or OIII, to enhance contrast and bring out the faint structures of the nebulae against the night sky.
Timing is also crucial for successful nebula observation. Plan your stargazing outings around the lunar cycle; a new moon or a period of minimal moonlight will provide darker skies, allowing fainter nebulae to shine more brightly. Additionally, the best time to observe is often during the winter months when the air is crisper and clearer, revealing more celestial detail.
Familiarize yourself with the constellations that house the nebulae you wish to observe. The Orion Nebula, for example, can be easily found in the famous constellation Orion, making it a perfect starting point for beginners. Using star charts or astronomy apps can help you locate not only prominent nebulae but also lesser-known ones that are hidden gems waiting to be discovered.
Lastly, patience and practice are key. Nebulae can be elusive and may require multiple observing sessions to fully appreciate their beauty. Take the time to soak in the experience, and don’t hesitate to join local astronomy clubs or online communities. Engaging with fellow enthusiasts can provide valuable insights, tips, and camaraderie as you embark on your cosmic journey.
By following these tips, amateur astronomers can unlock the mesmerizing beauty of nebulae, transforming their backyard into a portal to the cosmos and nurturing a lifelong passion for the wonders of the universe. Happy stargazing!
12. The Future of Nebula Research: Upcoming Missions and Technologies
As we stand on the brink of a new era in astronomical research, the future of nebula exploration is set to be transformed by a wave of innovative missions and advanced technologies. These advancements promise to deepen our understanding of these mesmerizing cosmic structures, providing insights into their formation, evolution, and the role they play in the broader tapestry of the universe.
One of the most anticipated missions is NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), which, launched in late 2021, is already revolutionizing our view of the cosmos. Equipped with state-of-the-art infrared capabilities, JWST allows astronomers to peer through the dust clouds of nebulae, revealing previously hidden details of star formation and the intricate processes that govern these celestial nurseries. Its ability to capture high-resolution images and spectra will enable researchers to study the chemical compositions of nebulae, shedding light on the building blocks of stars and planets.
Looking further ahead, missions such as the European Space Agency’s Euclid telescope aim to explore the mysterious dark energy that influences the expansion of the universe, while also capturing the essential role nebulae play in cosmic evolution. Additionally, advancements in ground-based observatories, such as the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) in Chile, are set to provide unprecedented views of nebulae with its advanced adaptive optics and massive aperture, allowing for sharper images and detailed studies.
Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning is poised to revolutionize nebula research. These technologies can sift through vast amounts of observational data, identifying patterns and anomalies that would be impossible for human researchers to detect alone. This could lead to new discoveries about the lifecycle of nebulae and their interactions with surrounding cosmic environments.
In conclusion, the future of nebula research is bright, fueled by ambitious missions and cutting-edge technologies. As we continue to explore these captivating regions of space, we can expect to unlock secrets that not only enhance our understanding of nebulae but also offer profound insights into the origin and evolution of the universe itself. The cosmos beckons, and with each new venture, we are one step closer to unraveling its mysteries.
13. Cultural Significance of Nebulae in Art and Literature
Nebulae, with their awe-inspiring beauty and enigmatic presence, have long captivated the imagination of artists and writers throughout history. These celestial wonders, often depicted as colorful clouds of gas and dust illuminated by the light of stars, serve as a rich source of inspiration in art and literature, reflecting humanity’s quest to understand the universe and our place within it.
In art, nebulae have been portrayed in various forms, from the swirling patterns of abstract paintings to the intricate details of digital renderings. Artists have sought to capture the ethereal quality of nebulae, often using vibrant colors that mirror the actual hues observed in astronomical images. The romantic notion of the cosmos has led many to create pieces that evoke a sense of wonder and exploration, inviting viewers to ponder the vastness of space and the mysteries it holds. The iconic “Starry Night” by Vincent van Gogh, for instance, while not a direct representation of a nebula, embodies the swirling motion and emotional depth that such celestial phenomena inspire.
In literature, nebulae often symbolize the unknown and the limitless possibilities of existence. Writers have drawn parallels between the beauty of nebulae and themes of creation, transformation, and the vastness of human experience. Science fiction, in particular, has embraced nebulae as backdrops for epic tales, serving as the setting for spacefaring adventures or as metaphors for the protagonists’ journeys into the unknown. authors like Arthur C. Clarke and Isaac Asimov have woven these cosmic clouds into their narratives, using them to explore profound philosophical questions about life, intelligence, and the universe.
Moreover, in many cultures, nebulae have been intertwined with mythology and symbolism. They often represent creation myths, the birth of stars, or the souls of the departed traveling through the cosmos. Indigenous cultures and ancient civilizations viewed the night sky as a canvas of stories, with nebulae playing a significant role in their cosmologies, guiding their beliefs about existence and the afterlife.
As we delve deeper into the mysteries of nebulae through astronomy, we also uncover the profound impact they have had on human creativity and thought. Their cultural significance in art and literature not only reflects our fascination with the cosmos but also serves as a reminder of our shared pursuit of knowledge, beauty, and understanding in a universe that is, at times, beyond comprehension.
14. Conclusion: The Wonders of Nebulae and Their Impact on Our Understanding of the Universe
In conclusion, nebulae are not merely beautiful cosmic phenomena; they are vital to our understanding of the universe and our place within it. These vast clouds of gas and dust serve as the birthplace of stars and planets, creating an intricate tapestry of celestial evolution that has fascinated astronomers for centuries. Each type of nebula, from the vibrant emission nebulae to the ethereal beauty of reflection and the ghostly remnants of planetary nebulae, tells a unique story about the life cycle of stars and the dynamic processes that shape our cosmos.
By studying nebulae, scientists glean critical insights into the fundamental processes of stellar formation and the chemical enrichment of the interstellar medium. They reveal the complex interplay between gravity, radiation, and the elements that forge the very building blocks of life. Moreover, nebulae challenge our perceptions and inspire curiosity, encouraging us to look deeper into the mysteries of the universe.
As we gaze at these distant wonders through our telescopes, we are reminded of the vastness of space and time, and the intricate dance of creation and destruction that defines our universe. Each nebula is a testament to the beauty and complexity of cosmic phenomena, urging us to explore further and expand our understanding of the universe. The wonders of nebulae not only enrich our scientific knowledge but also ignite our imagination, fostering a sense of wonder that connects us all to the cosmos. As we continue to explore these celestial marvels, we unlock the secrets of the universe, one nebula at a time.
As we conclude our journey through the captivating world of nebulae, we hope you’ve gained a deeper appreciation for these stunning cosmic phenomena. From the vibrant colors of emission nebulae to the intricate structures of planetary nebulae and the haunting beauty of dark nebulae, each type tells a unique story of stellar evolution and the birth of new celestial bodies. By understanding the intricacies of these majestic clouds of gas and dust, we not only enhance our knowledge of the universe but also ignite our imagination about the vastness of space. So, whether you’re an aspiring astronomer or simply a curious stargazer, we encourage you to continue exploring the cosmos. The skies above are filled with wonders waiting to be discovered—keep looking up!