Meiosis is a process of cell division that occurs in organisms that reproduce sexually.
Meiosis is an essential part of the life cycle of these organisms because it enables the production of gametes, or sex cells, which are required for sexual reproduction. The end result of meiosis is the production of four genetically diverse daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
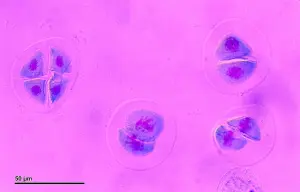
Meiosis begins with a parent cell that has two copies of each chromosome, one inherited from each parent. These chromosomes are lined up in pairs in the cell’s nucleus. During the first stage, called prophase I, the chromosomes condense and become visible under a microscope. They then pair up with their corresponding chromosomes to form tetrads.
The next stage, called metaphase I, is characterized by the alignment of the tetrads along the center of the cell. This is followed by anaphase I, during which the tetrads are separated and pulled to opposite ends of the cell. As a result, each daughter cell receives one copy of each chromosome.
Exchange of genetic material
The final stage of meiosis is called telophase I, and it involves the completion of cell division. The cell splits into two daughter cells, each with a full set of chromosomes. These daughter cells then enter a second round of cell division, called meiosis II. This one is similar to mitosis, a process that occurs in cells that do not reproduce sexually.
During meiosis II, the daughter cells produced in meiosis I undergo prophase II, metaphase II, anaphase II, and telophase II. As in mitosis, the chromosomes condense, align, separate, and are distributed into two daughter cells. However, unlike in mitosis, the daughter cells produced by meiosis II are genetically diverse because of the exchange of genetic material that occurs during the first stage.
The end result of meiosis is the production of four genetically diverse daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. These daughter cells, called gametes, are important for sexual reproduction. Indeed, they allow for the exchange of genetic material between parents and the production of offspring with a combination of traits from both parents. Without meiosis, sexual reproduction would not be possible, and the diversity of life on Earth would be greatly reduced.






